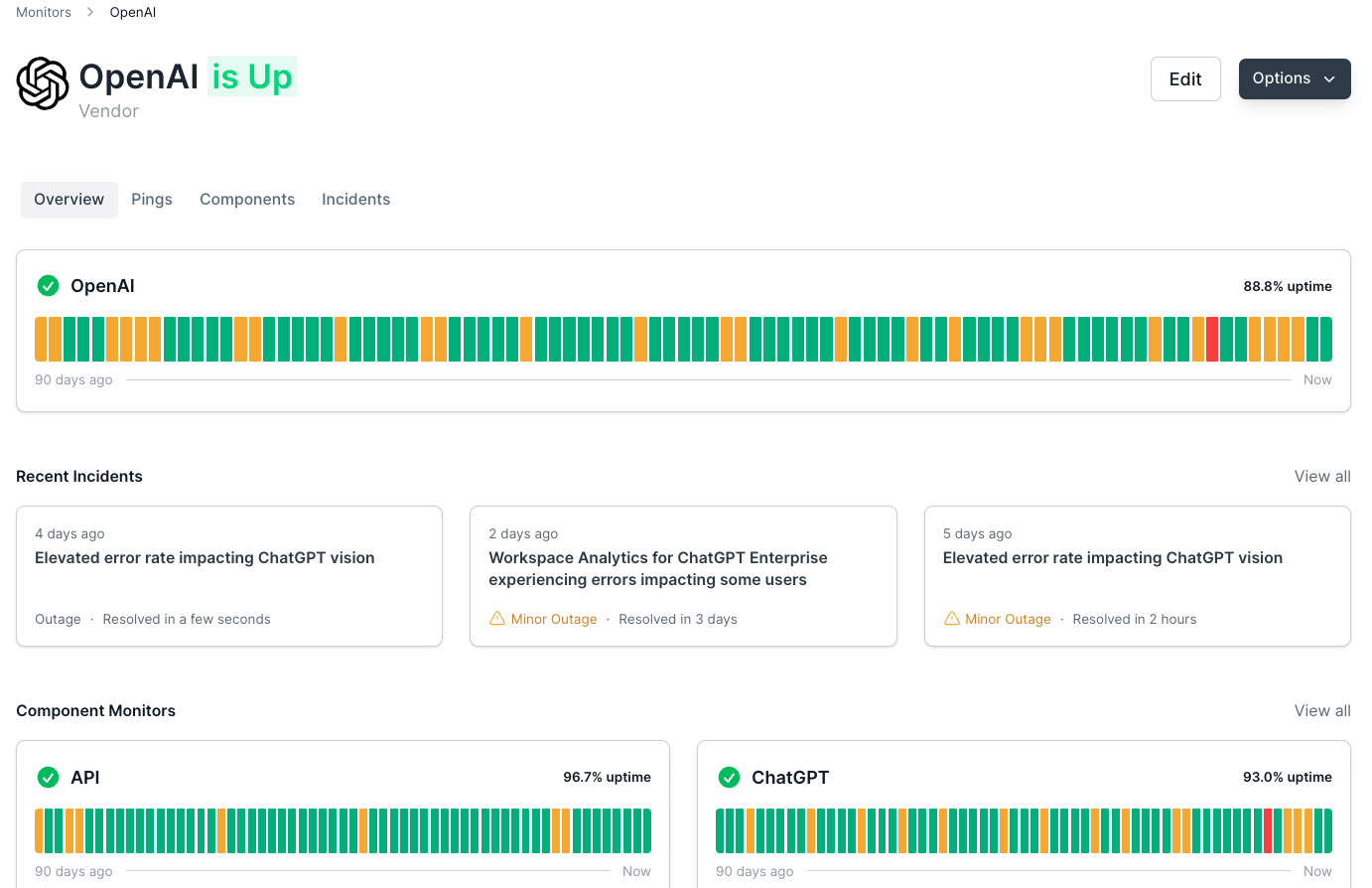
Introduction
A Java Map implementation is an collection that maps keys to values. Every Map Entry contains key/value pairs, and every key is associated with exactly one value. The keys are unique, so no duplicates are possible.
A common implementation of the Map interface is a HashMap:
Map<Integer, String> students = new HashMap<>();
students.put(132, "James");
students.put(256, "Amy");
students.put(115, "Young");
System.out.println("Print Map: " + students);
We've created a simple map of students (Strings) and their respective IDs:
Print Map: {256=Amy, 115=Young, 123=James}
A Java List implementation is a collection that sequentially stores references to elements. Each element has an index and is uniquely identified by it:
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList("James", "Amy", "Young"));
System.out.println(list);
System.out.println(String.format("Third element: %s", list.get(2));
[James, Amy, Young]
Third element: Young
The key difference is: Maps have two dimensions, while Lists have one dimension.
Though, this doesn't stop us from converting Maps to Lists through several approaches. In this tutorial, we'll take a look at how to convert a Java Map to a Java List:
- Convert Map to List of Map.Entry<K,V>
- Convert Map to List using Two Lists
- Collectors.toList and Stream.map()
- Stream.filter() and Stream.sorted()
- Stream.flatMap()
Convert Map to List of Map.Entry<K,V>
Java 8 introduced us to the Stream API - which were meant as a step towards integrating Functional Programming into Java to make laborious, bulky tasks more readable and simple. Streams work wonderfully with collections, and can aid us in converting a Map to a List.
The easiest way to preserve the key-value mappings of a Map, while still converting it into a List would be to stream() the entries, which consist of the key-value pairs.
The entrySet() method returns a Set of Map.Entry<K,V> elements, which can easily be converted into a List, given that they both implement Collection:
List<Map.Entry<Integer, String>> singleList = students.entrySet()
.stream()
.collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println("Single list: " + singleList);
This results in:
Single list: [256=Amy, 115=Young, 132=James]
Since Streams are not collections themselves - they just stream data from a Collection - Collectors are used to collect the result of a Stream's operations back into a Collection. One of the Collectors that we can use is Collectors.toList(), which collects elements into a List.
Convert Map to List using Two Lists
Since Maps are two-dimensional collections, while Lists are one-dimensional collections - the other approach would be to convert a Map to two Lists, one of which will contain the Map's keys, while the other would contain the Map's values.
Thankfully, we can easily access the keys and values of a map through the keySet() and values() methods.
The keySet() method returns a Set of all the keys, which is to be expected, since keys have to be unique. Due to the flexibility of Java Collections - we can create a List from a Set simply by passing a Set into a List's constructor.
The values() method returns a Collection of the values in the map, and naturally, since a List implements Collection, the conversion is as easy as passing it in the List's constructor:
List<Integer> keyList = new ArrayList(students.keySet());
List<String> valueList = new ArrayList(students.values());
System.out.println("Key List: " + keyList);
System.out.println("Value List: " + valueList);
This results in:
Key List: [256, 115, 132]
Value List: [Amy, Young, James]
Convert Map to List with Collectors.toList() and Stream.map()
We'll steam() the keys and values of a Map, and then collect() them into a List:
List<Integer> keyList = students.keySet().stream().collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println("Key list: " + keyList);
List<String> valueList = students.values().stream().collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println("Value list: " + valueList);
Check out our hands-on, practical guide to learning Git, with best-practices, industry-accepted standards, and included cheat sheet. Stop Googling Git commands and actually learn it!
This results in:
Key list: [256, 115, 132]
Value list: [Amy, Young, James]
This approach has the advantage of allowing us to perform various other operations or transformations on the data before collecting it. For example, knowing that we're working with Strings - we could attach an anonymous function (Lambda Expression). For example, we could reverse the bytes of each Integer (key) and lowercase every String (value) before collecting them into a List:
List<Integer> keyList = students.keySet()
.stream()
.map(Integer::reverseBytes)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println("Key list: " + keyList);
List<String> valueList = students.values()
.stream()
.map(String::toLowerCase)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println("Value list: " + valueList);
Note: The map() method returns a new Stream in which the provided Lambda Expression is applied to each element. If you'd like to read more about the Stream.map() method, read our Java 8 - Stream.map() tutorial.
Running this code transforms each value in the streams before returning them as lists:
Key list: [65536, 1929379840, -2080374784]
Value list: [amy, young, james]
We can also use Collectors.toCollection() method, which allows us to chose the particular List implementation:
List<Integer> keyList = students.keySet()
.stream()
.collect(Collectors.toCollection(ArrayList::new));
List<String> valueList = students.values()
.stream()
.collect(Collectors.toCollection(ArrayList::new));
System.out.println("Key list: " + keyList);
System.out.println("Value list: " + valueList);
This results in:
Key list: [256, 115, 132]
Value list: [Amy, Young, James]
Convert Map to List with Stream.filter() and Stream.sorted()
We're not only limited to mapping values to their transformations with Streams. We can also filter and sort collections, so that the lists we're creating have certain picked elements. This is easily achieved through sorted() and filter():
List<String> sortedValueList = students.values()
.stream()
.sorted()
.collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println("Sorted Values: " + sortedValueList);
After we sorted the values we get the following result:
Sorted Values: [Amy, James, Young]
We can also pass in a custom comparator to the sorted() method:
List<String> sortedValueList = students.values()
.stream()
.filter(value-> value.startsWith("J"))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println("Sorted Values: " + sortedValueList);
Which results in:
Sorted Values: [James]
If you'd like to read more about the sorted() method and how to use it - we've got a guide on How to Sort a List with Stream.sorted().
Convert Map to List with Stream.flatMap()
The flatMap() is yet another Stream method, used to flatten a two-dimensional stream of a collection into a one-dimensional stream of a collection. While Stream.map() provides us with an A->B mapping, the Stream.flatMap() method provides us with a A -> Stream<B> mapping, which is then flattened into a single Stream again.
If we have a two-dimensional Stream or a Stream of Streams, we can flatten it into a single one. This is conceptually very similar to what we're trying to do - convert a 2D Collection into a 1D Collection. Let's mix things up a bit by creating a Map<K,V> where the keys are of type Integer while the values are of type List<String>:
Map<Integer, List<String>> newMap = new HashMap<>();
List<String> firstName = new ArrayList();
firstName.add(0, "Jon");
firstName.add(1, "Johnson");
List<String> secondName = new ArrayList();
secondName.add(0, "Peter");
secondName.add(1, "Malone");
// Insert elements into the Map
newMap.put(1, firstName);
newMap.put(2, secondName);
List<String> valueList = newMap.values()
.stream()
// Aforementioned A -> Stream<B> mapping
.flatMap(e -> e.stream())
.collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(valueList);
This results in:
[Jon, Johnson, Peter, Malone]
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we have seen how to convert Map to List in Java in several ways with or without using Java 8 stream API.